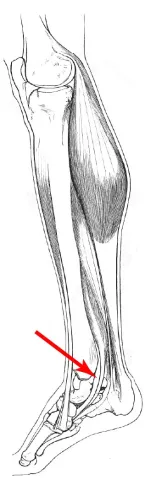
Tibialis Posterior serves as a key stabilizer in the lower leg, helping to support the arch of the foot and facilitate smooth movements during walking and running. It plays a crucial role in foot inversion and assists in plantarflexion of the ankle, essential for maintaining balance and proper gait. This muscle is situated deep within the calf and has tendons that run along the inner ankle and foot.
The name "Tibialis Posterior" comes from its location and function, with "tibialis" indicating its connection to the tibia (shinbone) and "posterior" denoting its position at the back of the leg.
Without the Tibialis Posterior, the foot would lack proper stabilization, leading to flatfoot deformity and compromised ability to control ankle movements effectively. This would result in difficulties with balance, pain during walking, and increased risk of injury to the foot and ankle.