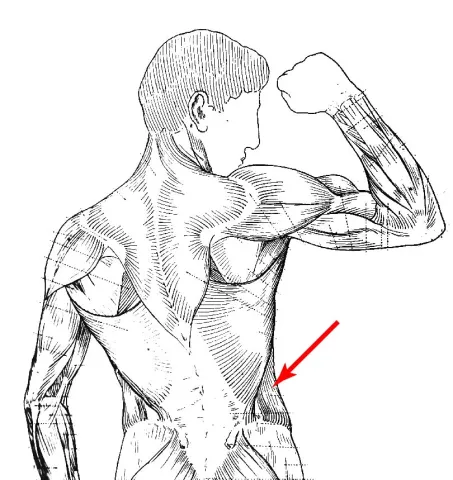
The external oblique is a large, thin sheet of muscle located on the lateral sides of the abdomen that forms the outermost layer of the abdominal wall. It functions to compress abdominal contents, rotate the trunk, and assist in lateral flexion of the spine. The external obliques work in conjunction with other core muscles to provide stability to the torso during movement and breathing.
The name "external oblique" derives from its anatomical position (external or superficial to deeper abdominal muscles) and its fiber direction, which runs obliquely or diagonally downward and inward. This directional orientation gives the muscle its distinctive angled appearance.
Without functioning external oblique muscles, humans would struggle with rotational movements of the trunk and would experience decreased core stability and compromised posture. Simple activities like turning the upper body, bending sideways, forceful exhalation during coughing or sneezing, and maintaining proper alignment during walking would become difficult or inefficient.