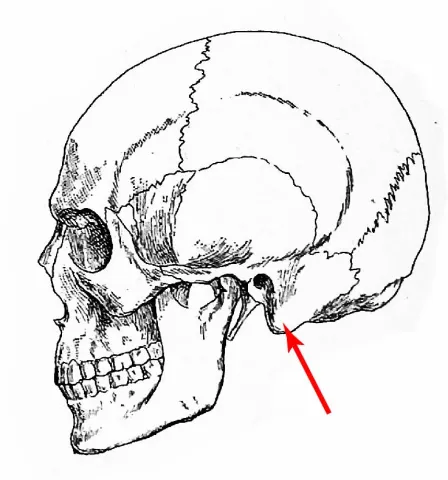
The mastoid process is a large, cone-shaped prominence projecting downward and forward from the temporal bone behind the ear. It serves as a crucial attachment point for several neck muscles, particularly the sternocleidomastoid muscle, which helps with head rotation and flexion. The mastoid process also contains air cells that connect to the middle ear and plays a role in sound conduction.
The term "mastoid" comes from the Greek word "mastos" meaning breast or nipple, plus "eidos" meaning form or shape, due to its nipple-like appearance. The word "process" comes from Latin "processus" meaning projection.