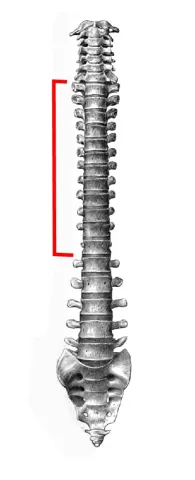
The thoracic vertebrae are the twelve bones in the mid-back that connect to the ribs, forming the backbone of the thoracic cage. They provide structural support, protect the spinal cord, and help maintain an upright posture. Their articulation with the ribs enables breathing by allowing chest expansion and contraction.
The term "thoracic" comes from the Greek thorax, meaning "chest," as these vertebrae form the upper part of the torso. "Vertebrae" is derived from the Latin vertere, meaning "to turn," emphasizing their role in movement.