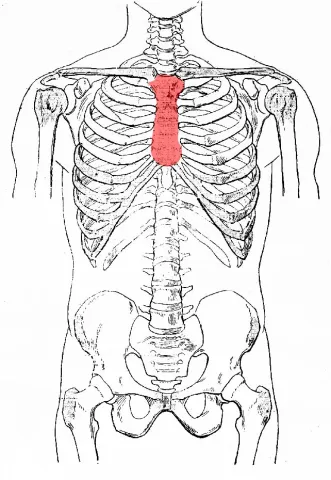
The sternum, or breastbone, is a flat, dagger-shaped bone that forms the central portion of the anterior chest wall, protecting vital organs like the heart and major blood vessels. It articulates with the ribs through costal cartilages and the clavicles, providing stability to the thoracic cage and upper limb movements. The sternum consists of three parts (manubrium, body, and xiphoid process) and serves as an important attachment site for muscles involved in breathing and upper body movement.
The word "sternum" comes from the Greek "sternon" meaning chest or breast. This direct etymological connection reflects its location in the center of the chest.